Photoelectric Sensor (Different Types, Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages)
Photoelectric sensors also named photo eyes sensors are devices that use optical properties to detect the distance, presence, or absence of an object, changes in the surface conditions, and position of objects. The sensor consists of an optical transmitter (often infrared) and a photoelectric receiver. The basis of the work of these sensors is based on the change in the amount of light received.
These types of sensors are other types of proximity sensors that operate on the basis of sending and receiving infrared waves.
These non-contacting sensors send modulated infrared waves and receive the reflection of these waves from different surfaces.
The use of pulse-modulated light increases the detection range of the sensor and also reduces the effect of ambient light on the sensor.
These sensors detect the light of any object, regardless of its type, and convert this light into electrical signals. It measures the physical quantity of light and then converts it into a readable form for the system.
Photoelectric Working Principle
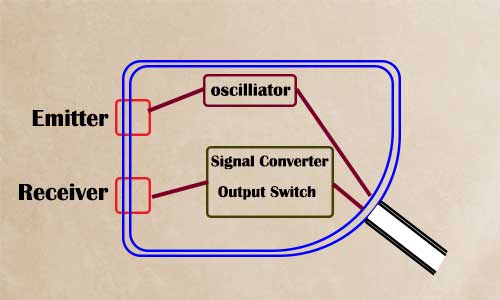
Photoelectric sensor basically has three main components:
- Emitter(LED) (Oscillator connected to a power source)
- The receiver of light (phototransistor)
- Output circuit (a signal converter and output switch connected to load)
An emitter is used for emitting light and a receiver for receiving light.
When the light beams emitted and sent by the sensor body are cut off or reflected, it changes the amount of light that reaches the receiver, then the receiver recognizes this change and confirms that it is from the emitter, and therefore triggers an output and converts it into an electrical output.
The output of a photoelectric sensor can have three type after activation, which are PNP, NPN or relays.
The ambient air in which the sensor is installed (especially industrial environments) may contain dust, smoke, and moisture. In this case, the sensor needs to send a stronger light.
Types of photoelectric sensors
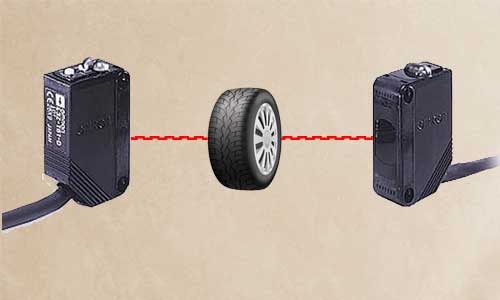
Through-beam Sensors
In this method, the photo sensor has two parts, a transmitter and a receiver, which are placed facing each other.
The transmitter sends a beam of light and the receiver receives that beam, which if an object passes between the beam of the transmitter and the receiver, the light is cut off and reduces the amount of light so the sensor senses the passage of the object.
This type of sensor has the longest switching distance among all types of optical sensors. They have a longer detection range than other types of photoelectric sensors.
This is because the light only has to move in one direction to reach the receiver from the emitter.
Applications of this type of sensor include:
- Industrial automation in the field of transportation
- Ceramic production industry (In cases where we are dealing with wide beams)
- Prevent accidents by installing sensors on both sides of the electric parking door.
Feature of Photo sensor Through-beam Sensors
- Constant performance and long operating distances vary from several centimeters to several tens of meters.
- The position of the measurement is not affected by changes in the path of the object under measurement.
- Performance is not affected by the brightness, color, or inclination of the object.
Disadvantage Photo sensor Through-beam Sensors
But this sensor also has disadvantages compared to the other two types.
It costs a bit more, requires more space for proper installation, because they have 2 components that require 2 cables and 2 pins, and therefore take up more space. and does not recognize thin transparent objects as well as the diffuse reflective model because light can reach the receiver directly through the object.
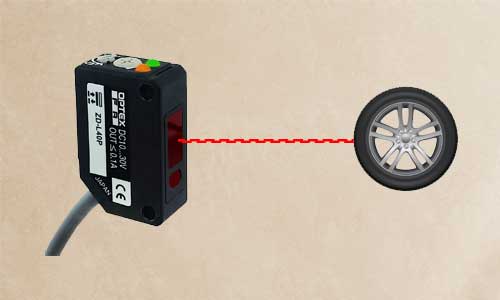
Diffuse-reflective Sensors
In this case, there is only the receiver and the transmitter, which are both mounted on one side, and the object acts as a reflector, thus light is sent by the transmitter.
If the object is in front of this light, reflections of it are emitted in space. Some of these reflections reach the receiver and the state of the output changes.
The switching distance of this sensor depends on the amount of reflected light.
Features of Diffuse-reflective Sensors
- Easy installation and adjustment
- One-piece housing and cost reduction
Disadvantage of Diffuse-reflective Sensors
- The most important disadvantage of using a diffuse sensor is that it has the shortest detection range compared to other types because it depends on the shape, size, and color of the object; it may not reflect light well to the sensor receiver.
- Error in the detection of colors that are too white or too black
- Less accuracy and reliability
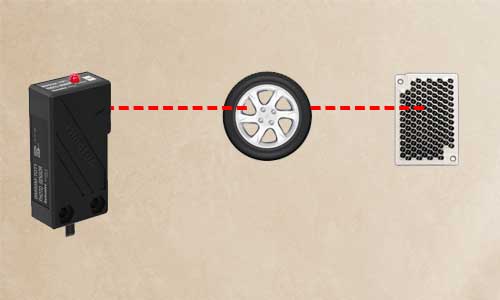
Retro-reflective Sensors
In this method, the sensor has a light reflector and the transmitter and receiver are on one side and the reflector is in front of it.
This reflector receives the light sent from the transmitter and reflects it to the receiver. If there is an object, the light does not reach the receiver and the sensor detects the presence of the object, and its output changes.
The switching distance of this sensor is higher than the Diffuse sensors but lower than through-beam sensors because the light must first hit a reflector and then return to the receiver. These types of sensors are the most widely used in factory automation.
Application for Retro-reflective Sensors
- Conveyor
- Identify empty and transparent bottles
- Gates and entrance doors
Feature
- Sensing distance ranges from several centimeters to several meters.
- Simple wiring and optical axis adjustment (labor-saving).
- Operation not greatly affected by the color or angle of sensing objects.
- Light passes through the sensing object twice, making these Sensors suitable for sensing transparent objects.
- Sensing objects with a mirrored finish may not be detected because the amount of light reflected back to the Receiver from such shiny surfaces makes it appear as though no sensing object is present. This problem can be overcome using the MSR function.
- Retro-reflective Sensors have a dead zone at close distances.
Disadvantage
- Some disadvantages of using a retro-reflective sensor are that you have to install this sensor with the reflector, if the object is shiny, the object may act as a reflector and so it will not be detected.
Features of photoelectric sensors
- Identify objects without direct contact and therefore long operating life
- Detect objects at long distances
- High switching speed from 30 microseconds to 30 milliseconds
- Recognize very small objects
- Recognize any object regardless of its kind, like glass, plastic, wood, and liquid
- Very short response time (less than one millisecond)
- High reliability, especially when fast part counting is required.
- Magnetic fields have no effect on them.
- Easy installation and adjustment
- The small size made them suitable for almost any application
- Price competitive
Disadvantage
Disadvantages of these sensors are:
- Dust, dirt, and stains will negatively affect the performance of these sensors.
- It has a blind spot.
Light sources generation
In different photoelectric sensors, and depending on their type, the light wave is generated in two ways:
Pulse Modulated Light
In this method, which is used by most photoelectric sensors, light is produced in specific time intervals and in the form of pulses.
In this way, the effect and interference of lights from other external sources are eliminated and there is no disturbance in the operation of the sensor.
Non-Modulated Light
In this method, which is mainly used by mark photoelectric sensors, light is sent at a constant density and continuously from the sensor.
The response time of these types of sensors is very short, but in contrast, their sensing distance is limited and they malfunction due to the effect of external lights.
Photoelectric sensor applications
Photoelectric sensors can be used in a wide range of different industries.
- Use in elevators to detect cabins
- Recognize the presence of people in different environments
- Use to detect parts in industrial factories
- Use in the electronics and semiconductor industries to detect glass layers
- Use to identify a variety of products in food automation
- Use in industrial conveyors to warn in case of problems
- Use to identify pallets for agricultural product lines
- Use to identify parts for cutting
- Use to determine the exact location of different cars
- Use to prevent textiles from twisting on the production line
- Detection of small objects in industrial environments
- Compare the contents of bottles, Detection of compounds inside metal cans
Want to know more about Photoelectric sensors? Click on the below link:
Top Photoelectric Sensors Suppliers and Manufacturers in the Middle East
Miniature photoelectric sensor detects carton position during packaging operations
Recent Posts
-
Booster Pump Troubleshooting and Maintenance: How to Fix and Prevent Common Issues
1. Introduction Imagine turning on your faucet only to be greeted with a weak trickle of water when …22nd Apr 2025 -
Energy-Efficient Booster Pumps: Selection and Tips for Maximizing Performance
1. Introduction Imagine never having to deal with fluctuating water pressure, noisy pumps, or skyroc …19th Apr 2025 -
Booster Pumps for Sustainable Water Systems: Irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting Solutions
1. Introduction Water scarcity is no longer a distant threat—it’s a reality affecti …16th Apr 2025




