How does a voltage tester check power lines in the shortest time and easiest way?
Are you tired of second-guessing whether a wire or electrical device is live or not? Do you want to ensure your safety and avoid the risk of electrical shock or damage to equipment? Look no further than the trusty voltage tester. This compact tool is a must-have for any electrician or DIY enthusiast, allowing you to quickly and easily determine whether there is voltage present in a circuit. In this blog post, we'll dive into the ins and outs of voltage testers, from the different types available to how to use them safely and effectively. We'll start by exploring the three main types of voltage testers: non-contact voltage testers, contact voltage testers, and digital multimeters. You'll learn how each of these tools works, as well as their pros and cons.
What is a Voltage Tester?
A voltage tester is a tool used to determine the presence or absence of an electric voltage in a wire, circuit, or device. It is a handheld device that allows electricians, DIY enthusiasts, and homeowners to test the electrical conductors in a safe and reliable way. Voltage testers come in various types, such as non-contact voltage testers, contact voltage testers, and digital multimeters, and are an essential tool for ensuring safety and preventing electrical accidents.

Fig 1. non-contact voltage tester
Voltage Tester Different Types
There are three main types of voltage testers:
- non-contact voltage tester
- contact voltage tester
- digital multimeter
Each of these types has its own pros and cons and is suited for different applications.

Fig 2. A non-contact voltage tester
Non-contact Voltage Tester
Non-contact voltage testers, also known as voltage detectors, are the most popular type of voltage tester. These testers work by detecting the electric field that is emitted by a live electrical conductor. They can detect voltage from a distance, without making contact with the wire or device being tested. Non-contact voltage testers are easy to use and can quickly indicate whether voltage is present or not. However, they are less accurate than other types of testers and cannot measure the exact voltage level.
Contact Voltage Tester
Contact voltage testers, also known as test lamps or test pens, require contact with the wire or device being tested. These testers work by completing a circuit between the tester and the electrical conductor. Contact voltage testers can provide more accurate readings than non-contact testers and can also indicate the level of voltage present. However, they require direct contact with the wire or device being tested, which can be dangerous if proper safety precautions are not taken.
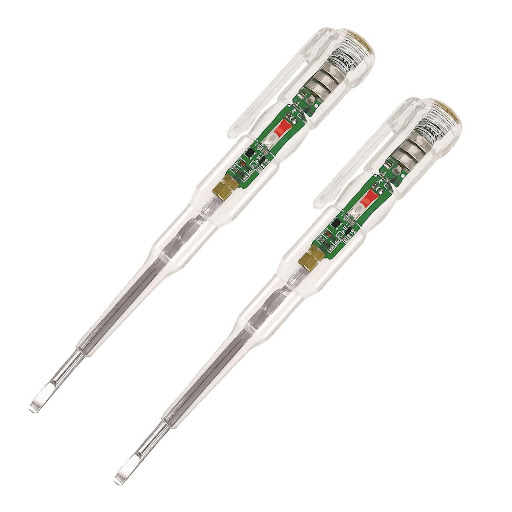

Fig 3. A contact voltage tester
Digital Multimeter
Digital multimeters are versatile tools that can be used to measure voltage, current, and resistance. They are more complex than non-contact or contact testers and require some knowledge of electrical circuits to use effectively. Digital multimeters can provide highly accurate readings of voltage levels and can be used for a variety of electrical applications. However, they are more expensive than other types of testers and can be less user-friendly.
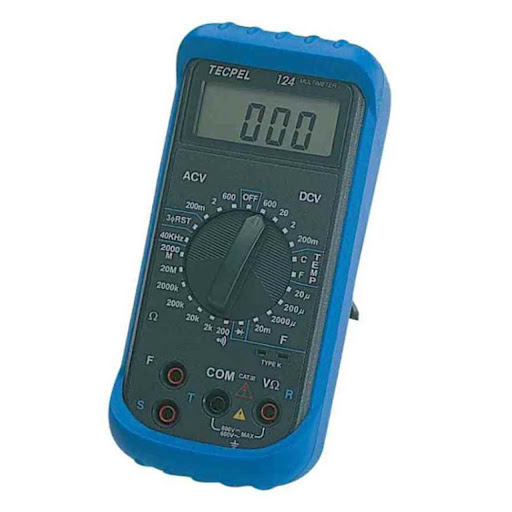

Fig 4. A digital multimeter
How to Use a Voltage Tester?
Before using a voltage tester, it is important to ensure that it is working properly. Check the batteries or power source, and make sure that the tester is calibrated correctly. Also, inspect the leads or probes for any damage or wear.
When using a non-contact voltage tester, hold the tester near the electrical conductor being tested, without making contact. The tester should emit an audible or visual signal if voltage is detected. Move the tester slowly along the wire or device being tested to ensure that the entire length is checked for voltage.
Fig 5. Power on the non-contact voltage tester.

Fig 6. Test the voltage tester on a working light.
Fig 7. Test an electrical outlet.
When using a contact voltage tester, first ensure that the device or wire being tested is not energized. Then, insert the tester's probes into the appropriate slots or contacts. The tester should indicate the presence of voltage if it is detected. It is important to keep the probes in contact with the wire or device being tested to ensure accurate readings.

Fig 8. Plug the voltage tester into the outlet
Fig 9. Read the results.
When using a digital multimeter, set the meter to the appropriate function, such as voltage measurement. Connect the leads or probes to the appropriate contacts or wires. The meter should indicate the voltage level being measured. Be sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when using a digital multimeter.

Fig 10. Plug in the multimeter and power it on.

Fig 11. Plug the black probe into the "COM" or "-" port.
Fig 12. Connect the red wire to the voltage port.

Fig 13. Selecting the voltage mode
It is important to take safety precautions when using any type of voltage tester. Always assume that a wire or device is energized until proven otherwise. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as insulated gloves and safety glasses. Make sure that the work area is well-lit and free of clutter. And never touch a wire or device being tested with your bare hands or metal objects.
In summary, using a voltage tester requires careful attention to safety and proper technique. Always check that the tester is working properly before use, and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Take appropriate safety precautions, and never assume that a wire or device is safe to touch without proper testing.
Troubleshooting with a Voltage Tester
A voltage tester can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting electrical problems in a variety of settings, from residential homes to industrial facilities. By using a voltage tester, you can identify whether voltage is present in a particular wire, device, or circuit, and narrow down the cause of the problem.
One common use of a voltage tester is to troubleshoot a circuit that is not working properly. For example, if a light fixture or outlet is not working, you can use a voltage tester to determine if voltage is present in the circuit. First, turn off the power to the circuit at the breaker box or fuse panel. Then, remove the cover plate from the outlet or switch, and test each wire in the circuit with a voltage tester. If voltage is present, the tester will indicate this. If voltage is not present, the problem may be with a faulty outlet or switch, or with a break in the wiring between the breaker box and the outlet.
Another use for a voltage tester is to troubleshoot a malfunctioning appliance. For example, if a refrigerator is not cooling properly, you can use a voltage tester to check the power supply to the appliance. First, unplug the refrigerator and locate the power cord. Test the cord with a voltage tester to ensure that it is delivering power to the refrigerator. If the power cord is delivering power, the problem may be with a faulty component inside the refrigerator, such as the compressor or thermostat.
A voltage tester can also be used to troubleshoot an electrical motor that is not working properly. For example, if a ceiling fan is not turning on, you can use a voltage tester to check the power supply to the fan motor. First, turn off the power to the fan at the breaker box or fuse panel. Then, remove the cover plate from the fan and locate the wires that connect the fan to the power supply. Test each wire with a voltage tester to determine if voltage is present. If voltage is not present, the problem may be with a faulty switch or wiring between the switch and the fan.
Maintenance and Care of Voltage Testers
To ensure accurate and reliable performance, it is important to properly maintain and care for your voltage tester. Here are some tips for maintaining and caring for your voltage tester:
Clean the tester regularly: Dust, debris, and moisture can build up on the tester, which can affect its performance. Use a soft cloth or a gentle cleaning solution to wipe down the tester regularly.
Check the battery or power source: If your voltage tester uses batteries, be sure to check them regularly to ensure that they are still working properly. If your tester uses a power source, be sure to check the cord and connections for any damage or wear.
Store the tester properly: When not in use, store your voltage tester in a dry, cool place, away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. Be sure to protect the leads or probes from damage by storing them in a separate compartment or pouch.
Calibrate the tester regularly: Over time, the accuracy of your voltage tester can be affected by factors such as temperature, humidity, and wear and tear. To ensure accurate readings, calibrate your tester regularly according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Replace damaged or worn components: If the leads or probes on your voltage tester become damaged or worn, replace them immediately. Damaged or worn components can affect the accuracy and safety of your tester.
Follow safety guidelines: Always follow appropriate safety guidelines when using a voltage tester, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and testing wires and devices before handling them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a voltage tester is an essential tool for anyone working with electrical systems, whether in a residential or commercial setting. By using a voltage tester, you can quickly and easily determine whether voltage is present in a wire, device, or circuit, and identify potential problems before they become more serious.
In this blog post, we've discussed the different types of voltage testers available, including non-contact testers, contact testers, and specialized testers for specific applications. We've also discussed how to use a voltage tester, including safety precautions and testing procedures, as well as troubleshooting common electrical problems using a voltage tester. Finally, we've provided tips for maintaining and caring for your voltage tester to ensure accurate and reliable performance.
Whether you're a professional electrician or a DIY homeowner, a voltage tester is an essential tool to have in your toolbox. By following the guidelines and recommendations in this post, you can use your voltage tester safely and effectively to diagnose and solve electrical problems with confidence.
To recap:
Q: What is a voltage tester?
A: A voltage tester is a tool used to detect the presence of voltage in an electrical circuit, wire, or device. It can be used to identify potentially dangerous electrical conditions and to troubleshoot electrical problems.
Q: What are the different types of voltage testers?
A: There are three main types of voltage testers: non-contact testers, contact testers, and specialized testers. Non-contact testers detect voltage without making physical contact with the wire or device being tested. Contact testers require physical contact with the wire or device being tested. Specialized testers are designed for specific applications, such as testing GFCI circuits or low-voltage systems.
Q: How do you use a voltage tester?
A: To use a voltage tester, follow these steps: 1) Turn off power to the circuit or device being tested. 2) Select the appropriate voltage tester for the application. 3) Follow the manufacturer's instructions for using the tester. 4) Test the wire or device being tested to determine if voltage is present.
Q: How do you troubleshoot electrical problems using a voltage tester?
A: To troubleshoot electrical problems using a voltage tester, follow these steps:
1) Identify the problem or symptom.
2) Turn off power to the circuit or device being tested.
3) Use the voltage tester to test the wires or components to determine if voltage is present.
4) Use the results of the tests to diagnose the problem and develop a plan for repair.
Q: How do you maintain and care for a voltage tester?
A: To maintain and care for a voltage tester, follow these tips: 1) Clean the tester regularly. 2) Check the battery or power source. 3) Store the tester properly. 4) Calibrate the tester regularly. 5) Replace damaged or worn components. 6) Follow safety guidelines.
Q: Why is a voltage tester important?
A: A voltage tester is important because it can help you detect potentially dangerous electrical conditions, diagnose electrical problems, and troubleshoot electrical systems safely and effectively. By using a voltage tester, you can ensure that electrical systems are functioning properly and avoid the risk of electrical shock or fire.
Recent Posts
-
Booster Pump Troubleshooting and Maintenance: How to Fix and Prevent Common Issues
1. Introduction Imagine turning on your faucet only to be greeted with a weak trickle of water when …22nd Apr 2025 -
Energy-Efficient Booster Pumps: Selection and Tips for Maximizing Performance
1. Introduction Imagine never having to deal with fluctuating water pressure, noisy pumps, or skyroc …19th Apr 2025 -
Booster Pumps for Sustainable Water Systems: Irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting Solutions
1. Introduction Water scarcity is no longer a distant threat—it’s a reality affecting millions …16th Apr 2025




